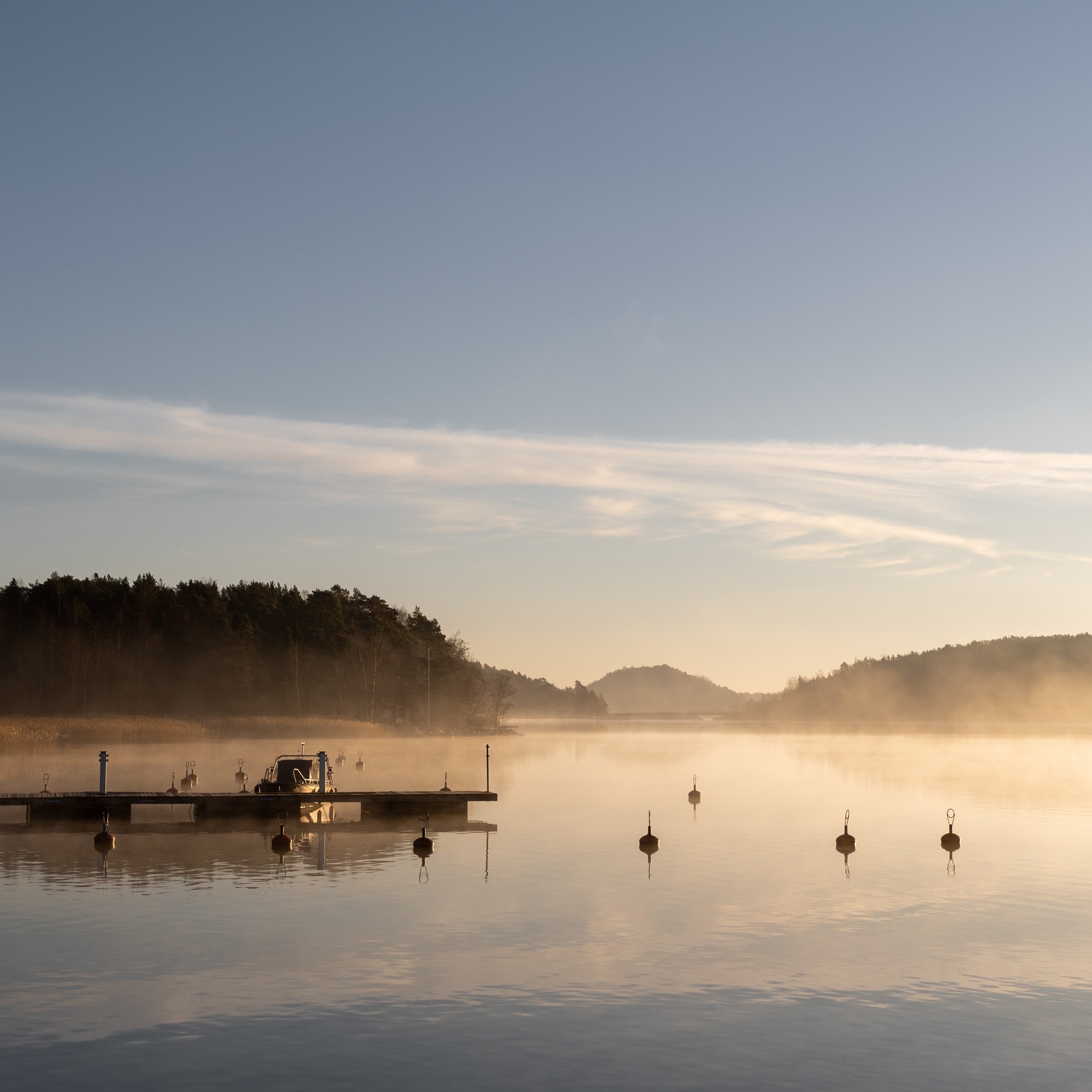

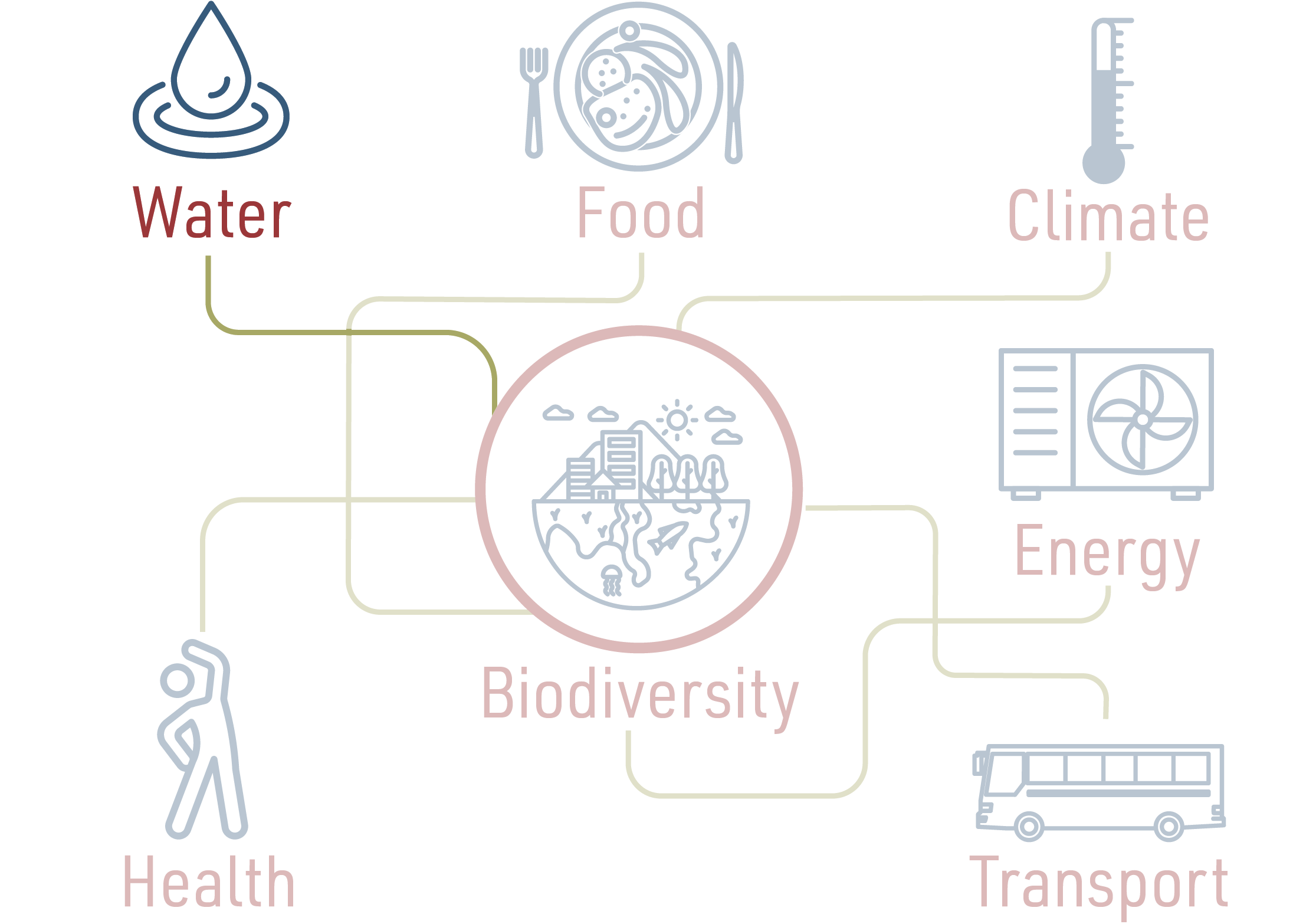
The biodiversity nexus: water
Water is closely interlinked with biodiversity. The integrity of ecosystems, such as forests, rivers, lakes, streams, wetlands, aquifers, and the marine environment, is dependent upon maintaining sufficient water quantity and quality. These ecosystems are also impacted by water management decisions. For example, groundwater overexploitation leads to intrusion of seawater rendering groundwater brackish and disrupting ecosystems, making it unusable for agricultural or domestic use. Wetlands and other natural ecosystems act as the “kidneys” of the landscape due to their ability to capture, store and transform pollutants and organics; water that flows through a wetland comes out cleaner! Floodplains and buffer strips offer dual benefits by regulating seasonal flows and curbing floods while also influencing local climates and replenishing groundwater through infiltration.
Water’s links to energy, health, and food
Water is also used for renewable energy production through hydropower and dams. However, these processes can impact river flow regulation and potentially jeopardize the ecological flow necessary for riverine ecosystems. On the other hand, a significant amount of energy is used to pump, heat, treat and transport water through our networks, while desalination and wastewater treatment are both quite energy-intensive.
The quality of water directly affects human and animal health; consuming water with emerging pollutants, xenobiotics or heavy metals has severe health implications On the other hand, conserving and restoring ecosystems offers a natural solution for providing clean drinking water.
Water is tightly linked to food production through irrigation and fisheries. However, the use of fertilizers and pesticides impacts the quality of natural water bodies leading to eutrophication and harmful algal blooms.
Charting a New Course
Embracing sustainable practices can revolutionize our water usage. Strategies such as sustainable green or hybrid grey-green infrastructure may support sustainable urban water drainage and storage. Wastewater reuse, multiple water qualities for various uses, and circularity in water use are sustainable practices that value all forms of water and lead to resilience in the face of climate change.
Related articles
The water team
-

Anna-Stiina Heiskanen
Finnish Environment Institute
-

Jari Koskiaho
Finnish Environment Institute
-

Jyri Mustajoki
Finnish Environment Institute
Firstname.lastname@syke.fi
-

Chrysi Laspidou
ATHENA Research Center
-

Anita Lazurko
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH)






The recently adopted European Union (EU) Nature Restoration Regulation is a new legislative development that represents the first time that legally binding EU-wide restoration targets and objectives have been set.